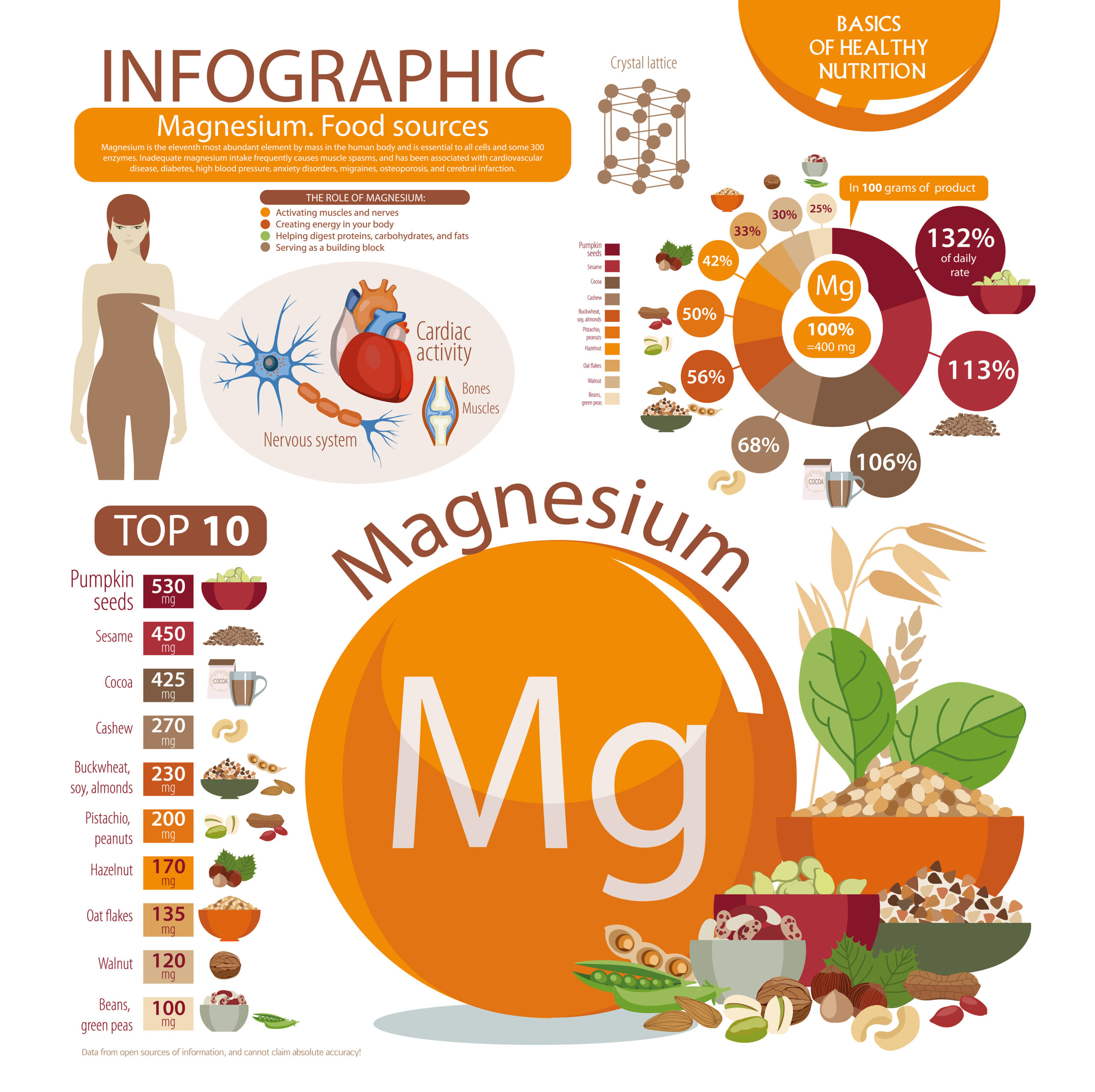
Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, yet it’s estimated that nearly half of all Americans are deficient in this essential nutrient. From supporting muscle and nerve function to regulating blood sugar levels and blood pressure, magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body.
In this guide, we explore the different types of magnesium supplements, their health benefits, and how to incorporate them into your daily routine.
Types of Magnesium
By understanding the different types of magnesium supplements and their respective benefits, you can make informed decisions about incorporating magnesium into your daily routine to support overall health and well-being.
When choosing a magnesium supplement, look for one that contains magnesium citrate, glycinate, or threonate, as these forms are more easily absorbed by the body. Start with a low dose and gradually increase it to avoid gastrointestinal side effects.
It’s highly recommended to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Magnesium Oxide
This form of magnesium is commonly found in over-the-counter supplements. While it has a high magnesium content, it’s not as easily absorbed by the body, making it less ideal for those with magnesium deficiency.
Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate is bonded to citric acid, which helps enhance its absorption. It’s often used as a laxative to relieve constipation and can also help support overall digestive health.
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is highly absorbable and less likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects. It’s a great option for individuals looking to increase their magnesium intake without the risk of digestive issues.
Magnesium Chloride
This form of magnesium is commonly found in topical magnesium products, such as sprays and lotions. It can also be taken orally and is known for its high bioavailability.
Magnesium Threonate
Magnesium threonate is believed to be highly absorbable and capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. This makes it a promising option for supporting cognitive function and brain health.
Magnesium Orotate
This form of magnesium is bonded to orotic acid and is believed to have cardiovascular benefits.
Magnesium Sulfate
Also known as Epsom salt, magnesium sulfate is often used in baths for muscle relaxation. It can also be taken orally in some cases.
Health Benefits of Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral with numerous health benefits. While individual experiences may vary, many people have reported positive experiences with magnesium supplementation. Some have found that it helps improve sleep quality, reduce muscle cramps, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Magnesium interacts with several other nutrients in the body, including calcium and vitamin D. It’s important to maintain a balance of these nutrients to ensure optimal health. Too much calcium, for example, can interfere with magnesium absorption, so it’s important to consider your overall nutrient intake when supplementing with magnesium.

Mood and Stress Management
Magnesium is known to help regulate neurotransmitters involved in mood and stress response, making it beneficial for mental health.

Muscle and Nerve Function
Magnesium plays a key role in muscle contraction and relaxation, making it essential for athletic performance and recovery.

Heart Health and Blood Pressure
Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure and supports cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Bone and Joint Health
Magnesium is involved in bone formation and helps maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.

Blood Sugar Regulation
Magnesium plays a role in insulin metabolism, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Does magnesium help with joint pain?
Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones and joints. It helps regulate calcium levels in the body, which is essential for bone health. Some studies suggest that magnesium supplementation may help reduce inflammation and pain associated with conditions like arthritis. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of magnesium on joint pain.
Does magnesium help with sleep?
Magnesium is often touted as a natural remedy for improving sleep quality. It plays a key role in regulating the body’s internal clock and promoting relaxation. Magnesium deficiency has been linked to insomnia and poor sleep quality. Supplementing with magnesium may help improve sleep by regulating neurotransmitters and melatonin production. Some people find that taking magnesium before bed helps them relax and fall asleep more easily.
Does magnesium help with leg cramps?
Leg cramps are often caused by muscle fatigue or dehydration. Magnesium is essential for muscle function and may help prevent or alleviate leg cramps. It helps relax muscles and maintain proper muscle function, which can reduce the frequency and severity of leg cramps. However, individual responses to magnesium supplementation may vary, so it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Does magnesium help with restless leg syndrome?
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. Some studies suggest that magnesium deficiency may be linked to RLS. Supplementing with magnesium may help improve symptoms of RLS by supporting muscle function and promoting relaxation. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of magnesium on RLS.
Does magnesium help with anxiety?
Magnesium plays a role in regulating neurotransmitters and is involved in the body’s stress response. Some studies suggest that magnesium deficiency may be linked to anxiety disorders. Supplementing with magnesium may help reduce anxiety symptoms by promoting relaxation and reducing the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. However, more research is needed to confirm these effects.
Does magnesium help with constipation?
Magnesium is often used as a natural remedy for constipation. It has a laxative effect and can help relax the muscles in the intestines, making it easier to pass stool. Magnesium citrate is commonly used for its laxative properties. However, it’s important to use magnesium supplements for constipation only under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as excessive magnesium intake can lead to diarrhea and other gastrointestinal issues.
Does magnesium help with weight loss?
Magnesium plays a role in metabolism and energy production, but there is limited evidence to suggest that magnesium supplementation alone can lead to weight loss. Some studies suggest that magnesium deficiency may be associated with obesity, and supplementing with magnesium may help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels, which could indirectly support weight loss efforts. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of magnesium on weight loss.
Does magnesium help with headaches?
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to migraines and tension headaches. Some studies suggest that magnesium supplementation may help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches, particularly migraines. Magnesium helps relax blood vessels and regulate neurotransmitters, which are believed to play a role in the development of headaches. However, individual responses to magnesium supplementation may vary, and it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Does magnesium help with Gitelman Syndrome?
Top 10 Food Sources of Magnesium
Magnesium is found naturally in many foods, making it easy to incorporate into your diet. Some of the best food sources of magnesium include:
- Fruits: Fruits like figs, raisins, and dates are relatively high in magnesium compared to other fruits.
- Leafy green vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium. Other vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and peas also contain magnesium, although in smaller amounts compared to leafy greens.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds are all high in magnesium.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, buckwheat, and whole wheat are good sources of magnesium.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in magnesium.
- Avocado: Avocado is a nutrient-dense fruit that contains magnesium.
- Bananas: Bananas are a good source of magnesium, as well as potassium.
- Dark chocolate: Dark chocolate contains magnesium, along with other beneficial nutrients.
- Fatty fish: Fish like salmon and mackerel are not only high in magnesium but also rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese contain magnesium, although the amount may vary depending on the processing.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help ensure you’re getting an adequate amount of magnesium naturally.

Are You Magnesium Deficient?
Who Should Take Magnesium and How Often?
Despite its importance, many people are deficient in magnesium. Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can include muscle cramps, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat. Supplementing with magnesium can help alleviate these symptoms and restore magnesium levels to normal.
Magnesium can be taken at any time of day, but some people find it beneficial to take it before bed to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. It’s generally safe for most people to take magnesium supplements, but individuals with kidney disease or certain medical conditions should consult with their healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Certain populations may benefit more from magnesium supplementation than others. Athletes, for example, may need more magnesium to support muscle function and recovery. Pregnant women may also benefit from magnesium supplementation to help reduce the risk of preterm birth and preeclampsia. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as migraine headaches or fibromyalgia, may also benefit from magnesium supplementation to help alleviate symptoms.
Adverse Side Effects and Precautions
While magnesium is generally safe, high doses can cause gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea and abdominal cramping. It’s important to start with a low dose and gradually increase it to avoid these side effects. Additionally, magnesium can interact with certain medications, so it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting supplementation.

The Magnificent Benefits of Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions. From supporting muscle and nerve function to regulating blood sugar levels and promoting relaxation, magnesium is essential for overall health and well-being. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet and considering supplementation if needed can help ensure you’re getting enough magnesium to support optimal health.
Whether you’re looking to improve your sleep, alleviate muscle cramps, reduce anxiety, or support bone health, magnesium may offer a natural solution. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
By understanding the different types of magnesium supplements, their health benefits, and how to incorporate them into your daily routine, you can make informed decisions about your magnesium intake. Remember, everyone’s magnesium needs are different, so listen to your body and work with your healthcare provider to find the right balance for you.